Interactive Online Tutorial Sheets
Tutorial Sheet Nine Moments of Inertia
Q1: An electric motor supplies a power of $200W$ to drive an unloaded flywheel of moment of inertia $2kgm^2$ at a steady speed of $600revmin^{-1}$. How long will it be before the flywheel comes to rest after the power is switched off assuming the frictional couple reamins constant?
| Hints | |
|---|---|
$Power = Torque \times Speed$ |
|
$T=I\theta$ |
|
$V = u + at$ |
Q2: A figure skater is spinning about a vertical axis with his arms extended vertically upwards. Will he spin faster or slower when he allows his arms to fall until they are horizontal? Has his kinetic energy increases or decreased? How do you account for the change?
A horizontal disc rotating freely about a vertical axis has a speed of $90revmin^{-1}$. A small piece of putty of mass $0.02kg$ falls vertically on to the disc and sticks to it at a distance of $50mm$ from the axis. If the speed is thereby reduced to $80revmin^{-1}$ calculate the moment of inertia of the disc.
| Hints | |
|---|---|
$Momentum = I\omega$ |
|
Does the skater put in energy when he/she lifts or lowers their arms? |
|
Initial Momentum $= I_1\omega_1$ |
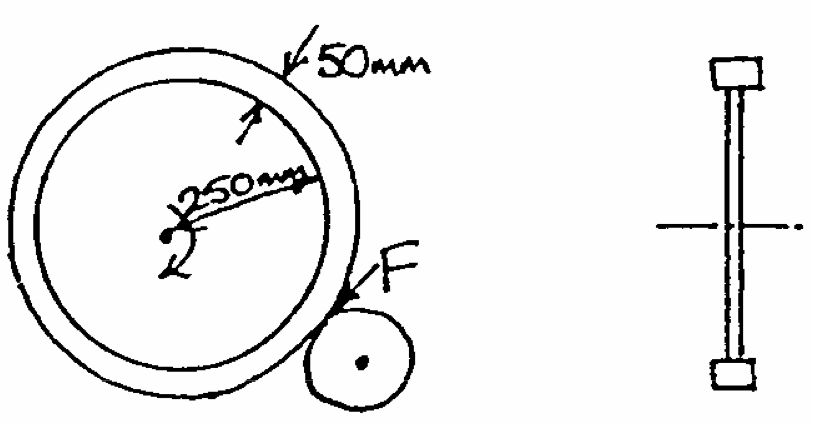
Q3: The flywheel shown in the figure is acted on a by roller which produces a force of $10N$. What is the angular acceleration? Assume that 90% of the flywheel mass lies in the rim at a radius of $0.275m$ and the total mass is 10kg.
How fast must the flywheel rotate in order to store 50 Joules of energy? What is the rim speed and how long does it take to raise the flywheel to speed?
| Hints | |
|---|---|
Approximate Inertia $=0.9Mr^2$ |
|
Find the torques and kinetic energy of the rotating disc |
|
Calculate the angular speed for 50 Joules and then calculate rim speed. Use constant acceleration equations to find time the raise the speed. |
Q4: A drum is driven by a rope of length $20m$. If the diameter of the drum is $0.5m$ and its moment of inertia about the centre of gravity os $0.1kgm^2$ what is its maximum speeds if the tension in the rope is $10N$?
| Hints | |
|---|---|
Work Done = Force $\times$ Distance |
|
Final kinetic Energy = $I\omega^2$ |
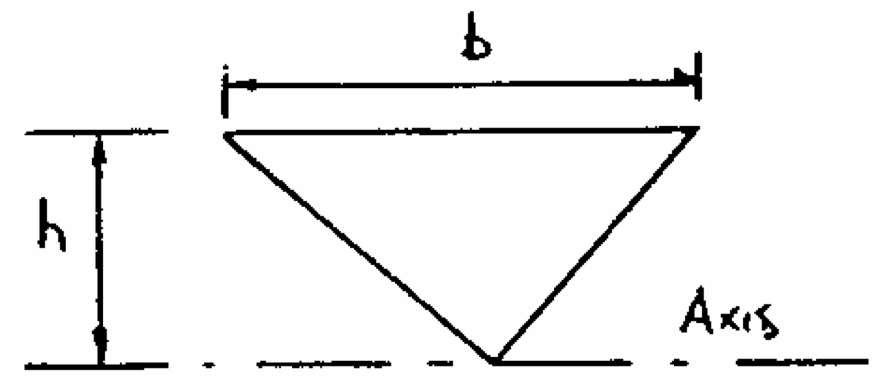
Q5: Determine from first principles the moment of inertia of a thin plate of mass per unit area $\rho t$, cut into a triangular shape as shown, about an axis passing through the apex and parallel to the base. What is the corresponding radius of gyration?
| Hints | |
|---|---|
$I = \int x^2 \mathrm d m$ |
|
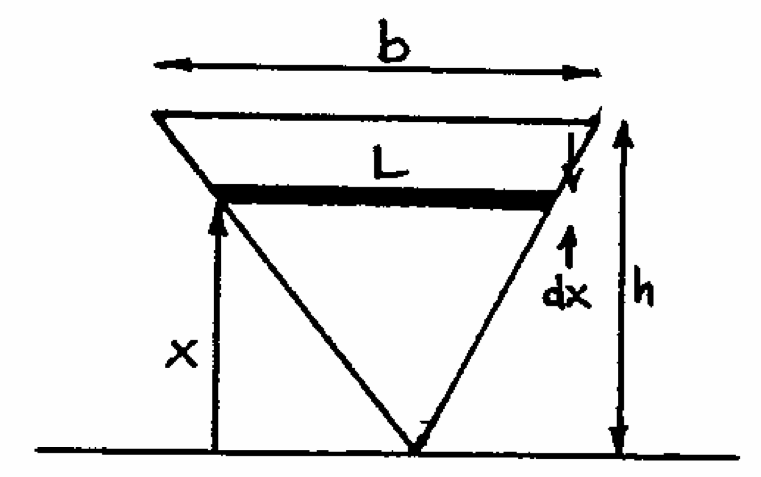 Work out: Mass of Element ($\mathrm d m$) in terms of $x \mathrm d x$ |
|
$I = \int x^3 \rho \frac{tb}{h} \mathrm d x$ |
Q6: The pendulum of a clock is made from a circular steel bar of $10mm$ diameter and length $250mm$. On its end is a $50mm$ cube of steel. If the density of steel is $7850kgm^{-3}$ what is the pendulum moment of inertia if it is pivoted about one end? The inertia of a uniform rod, through the centre of gravity is $\frac{ml^2}{12}$. If the pendulum amplitude is $15$ degrees and the maximum potential energy during the stroke is $0.1J$ what is the pendulum mid stroke angular velocity?
| Hints | |
|---|---|
$m = \frac{\rho\pi D^2 L}{4}$ |
|
$I = \frac{ml^2}{12}$ |
|
$I_{\mathrm{hinge}} = I_{\mathrm{centre of gravity}} + mx^2$ |
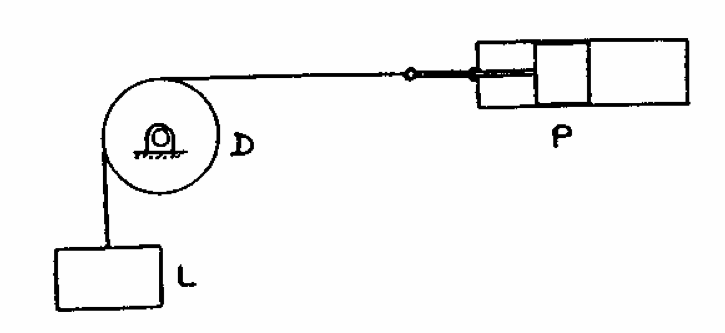
Q7: The figure shows a load L of mass $12kg$ being lifted by a light cable which passes a number of times around a drum D of radius $0.26m$ and thence to the piston P of an air cylinder. The radius of gyration of the drum is $0.2m$. The mass of the drum is $15kg$ and the mass of the piston is $8kg$. The force of air on the piston is $210N$; the frictional force on the piston is $5N$ and the frictional torque on the drum is $13Nm$. Draw free body diagrams for L, D and P and hence determine the angular acceleration of the drum.
| Hints (Scroll) | |
|---|---|
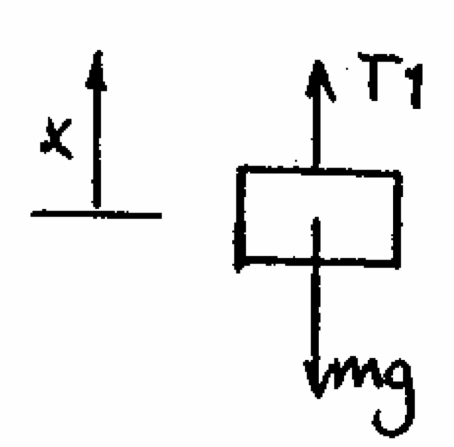 |
|
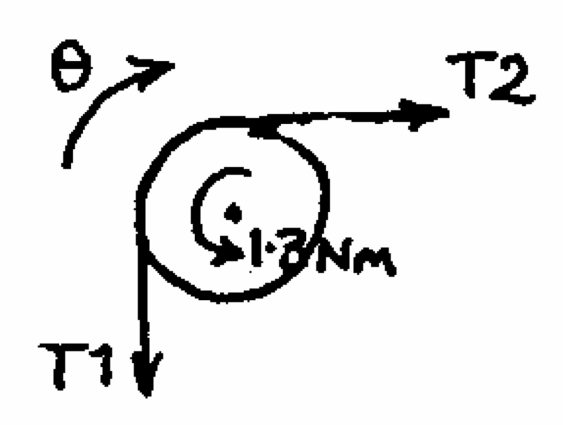 |
|
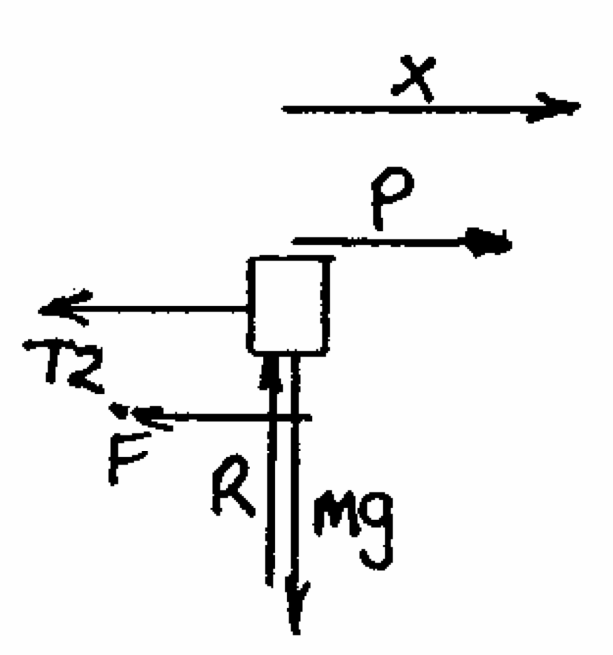 |